Polycythemia is a condition that results in an increased red blood cell volume circulating throughout your bloodstream. Those with this condition may have an increase in hematocrit, hemoglobin, or their red blood cell count in general. For polycythemia to be considered in women, their hematocrit or HCT has to be greater than 48% and in men 52%. If the hemoglobin levels are greater than 16.5g/dL in women or 18.5g/dL in men, then it is considered as well.
Two Categories
Polycythemia is divided by two categories; primary and secondary. Primary occurs when a genetic mutation or abnormality is present. Most people diagnosed with polycythemia have a mutation in their JAK2 gene. Though most cases are not hereditary, some cases are. Lastly, it is common for the TET2 gene to have mutations in the polycythemia cells. Secondary occurs in those who have experienced low levels of oxygen in their bloodstream for a long period of time. Because of the extended lack of oxygen, the body will make too much of the erythropoietin hormone. If there is too much of this hormone then too many red blood cells will be made.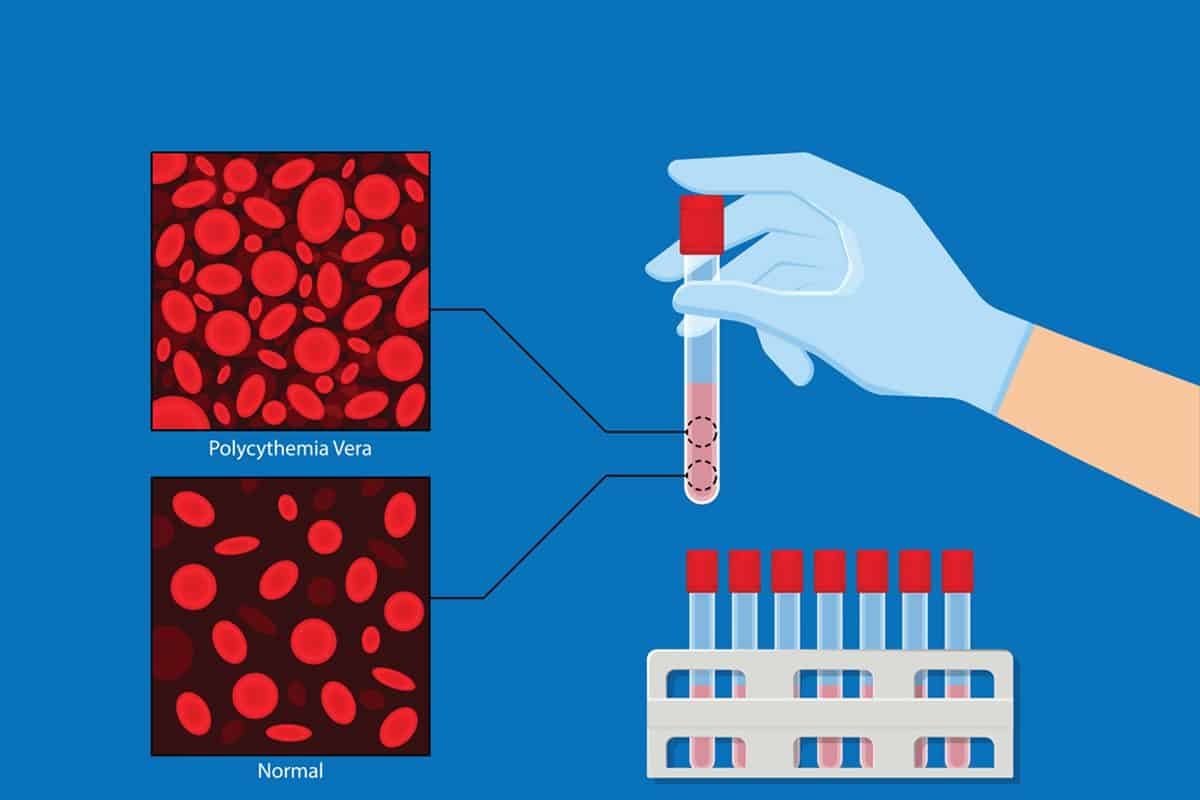
Signs and Symptoms
Because every case is unique, some people may have no to minimal symptoms. General symptoms include:
- Tiredness and Weakness
- Difficulty breathing when lying down
- An enlarged spleen
- Blurry or double vision
- Itchy skin, typically after following a warm bath
- Your skin is reddish/purple
- Bleeding gums
- Weight loss
- Tinnitus
- Sweating, even more so at night
Those affected may also have other blood disorders. In most cases this is very common. Also, bleeding issues and clotting may occur too.
Risk Factors
Every condition comes with risk factors and polycythemia is no different. Risk factors include; a history of blood clots, being over 60, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, and being pregnant. Also, if your blood is thicker you’re more at risk because clots are more able to form this way.
Treatment
Though there is no cure, treatment can help manage any symptoms while helping prevent complications. Depending on your case, your doctor will develop a plan that works for you. But because there are high risk cases and low risk cases, the treatments can look different.
Low Risk
Those who are low risk at contracting blood clots, their treatment includes two things; aspirin and a phlebotomy. Low dose aspirin affects your blood platelets which decreases your risk of forming blood clots. A phlebotomy is when your doctor uses a needle to remove a small amount of blood from a vein. In return, this helps reduce your red blood cell count. This can be done once a month every few months until your levels are closer or back to normal.
High Risk
While aspirin and a phlebotomy may be done as well, those who are high risk require more treatment that is specialized to their case. Treatments include:
- Hydroxyurea.
- This cancer drug helps prevent the body from making too many red blood cells. Using this treatment method helps reduce your risk of blood clots. This is an off-label drug used to treat polycythemia.
- Interferon Alpha.
- Your immune system is able to fight off overactive bone marrow cells thanks to this type of drug. It also can help block the body from making too many red blood cells. Much like the drug above, this is also an off-label drug used to treat.
- Busulfan
- While this drug is approved to help treat Leukemia, it is also used off-label to treat polycythemia.
- Ruxolitinib
- If you cannot tolerate hydroxyurea or your blood count is not lowered enough, your doctor may prescribe this drug. This drug works by inhibiting growth factors that are responsible for creating red blood cells and functioning the immune system. Also, it is the only approved drug to treat polycythemia.
Though polycythemia is not curable, it is treatable. Helping treat this condition decreases your chance of dangerous blood clots, increased red blood cell volume, and other risky complications. Talking to your doctor is the best option to do. If you feel like they’re not giving you everything you need try seeing a different doctor or a specialist. Getting the best care possible will help improve your quality of life!